Cannabinoid & Terpene Production
Sugars, saccharides, and carbs (carbohydrates) are all the same thing and a miracle of it all is that plants themselves manufacture their own energy in the form of carbohydrates. The production of carbohydrates (sugars) in plants through photosynthesis is a vital process, and the sugars (glucose, sucrose) produced through that process play a pivotal role in the plants metabolism, growth rate, development, and yields.
Most Cannabis Cultivators are surprised when they learn that adequate levels of sugars (glucose, sucrose) must be present in significant amounts for the plant to properly develop and progress through each stage of the photoperiod. The transitions between each developmental stage, seedling to juvenile development, vegetative juvenile to vegetative adult, and from vegetative adult to flowering adult all must have adequate levels of sugar to ensure proper development.
Condensation Reaction
During early organ development of the cannabis plant, glucose, and fructose, simple 6-carbon sugars are formed and are associated with early organ growth and the metabolism of the plant. These simple carbohydrates provide early nutrient reserves critical for development of seedlings first true leaves and is used in respiration to release energy for use by the plant’s cells. These simple sugars are soluble and transported throughout the plant.[i]
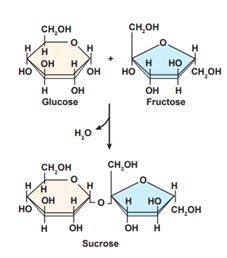
Sucrose is a 12-carbon simple sugar molecule composed of glucose and fructose after transpiration (removal of water in the plant) and is the final product of photosynthesis. Sucrose is produced naturally in plants and is closely associated with the maturity, differentiation, and full functionality of plant organs. Figure 1 illustrates the bond of monosaccharides glucose and fructose into the disaccharide sucrose by the removal of water. Sucrose is produced in the mesophyll cells of plant leaves (as well as other organs) by the action of sucrose phosphate synthase and sucrose phosphate phosphatase or by sucrose synthase. By forming the more complex sugar, sucrose. The plant is able to store energy more efficiently in a more compact form as the disaccharide. Sucrose is actively transported into the phloem by the companion cells. The sucrose then diffuses into the neighboring sieve tube cells throughout the plant.
These disaccharides are carbohydrates that fuel healthier, higher-yielding cannabis plants. Cannabis plants use photosynthesis to create carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are the primary internal energy source for cannabis plants. But being an energy source isn’t all those carbohydrates do inside your cannabis plants. Your plants use carbohydrates to create roots, stems, leaves, and buds, and to maintain genetic integrity.
Plant Structure & Bud Formation

Cannabis’s carbohydrate metabolism is part of the process that forms THC and other cannabinoids, as well as terpenoids. If the Cannabis plant detects that insufficient carbon (primarily sucrose) exists, the plant is deemed “incompetent” to complete the next developmental program and developmental transition is delayed or discontinued.
These carbohydrates also contribute to the cellular structure of plants. In the case of cannabis, sugars contribute to almost 80% of the plant’s structure. These kinds of sugar carbohydrates are known as “structural carbohydrates”. They function as vital building blocks, helping to develop cell walls throughout the plant. Glucose is used by plants for energy and to make other substances like cellulose and starch. Cellulose is used in building cell walls and helping the plant maintain structural integrity.[ii]
It is crucial for your cannabis plants store carbohydrates for use during bloom phase. They do this because bloom phase is when reduced light hours and other factors diminish the amount of carbohydrates they can newly produce. Almost all cannabis carbohydrate production and storage happen during grow phase and the first 1-3 weeks of bloom phase. Then it pretty much stops. This stoppage of carbohydrate production can starve your plants.
Your plants need lots of carbohydrate energy to produce flowering buds and cannabinoids. This is especially true when you’re pushing your plants with a high DLI, supplemental CO2, high-PPM feed programs and intense cultivation tactics.
A well-fed cannabis plant with well-stocked sugar reserves will develop thick, potent, and resinous buds. Maximizing sugar production and sugar reserves is essential to maximizing terpene and resin production in buds and maximizing your yields. When you feed your plant carbohydrates during the bloom photoperiod, your plants get a necessary energy burst that helps them create bigger buds, an increased cannabinoid production, higher terpene profile, and increased THC potential.
This cannot be done effectively through foliar applications but rather through the soil horizon to the root system. Julian Karadjov, PhD, confirms in his studies that plant roots efficiently absorb carbohydrates, all for a safeguard of your crops, and energize microbes in the soil to perform at an increased level.[iii]n
Optimal Cannabis Carbohydrate Status for Photoperiod Transition
In a vacuum of perfect conditions, Carbohydrate deficits would not exist. Your plants would have enough energy through photosynthate production. The levels of carbohydrates would be sufficient to provide stable growth, development, and function as well as yield all while providing glucose for adequate respiration.
Unfortunately, nutrient deficiencies and stresses in the plant’s environment do not provide these perfect conditions for growth. Stresses like increased light, temperature fluctuations, salinity, and nutrient load can adversely affect the photosynthetic metabolism of the plants. With this adversity the plants production will fall into non-optimum levels reducing production results.
Optimal cannabis production must balance carbohydrate production from photosynthesis, the amount of carbohydrates based on environmental conditions and energy requirements through respiration and hold adequate carbohydrate reserves from the vegetative to blooming photoperiod by being able to efficiently allocate and store an excess through photosynthate production.
Good Medicine Compost Plus Coffee-K
Good Medicine Compost plus Coffee-K is an all-natural flowering compost that is designed to specifically boost the complex processes involved with bud development during the good grow. The inclusion of Coffee-K, a proprietary organic fertilizer developed by Mayer Materials, promotes the conversion and uptake of deficient, unavailable, and insoluble fractions of nutrients that plants otherwise would not be able to consume during the important flowering stages of the good grow resulting in higher potency accompanied by complex flavors and aromas.
Coffee-K is an organic acid and enzyme nutrient cycling booster exclusive to Comanche Compost Co., built to deliver large amounts of phosphorous and potassium precisely to the flowering stages. The proprietary blend allows for an increased carbohydrate delivery into the root zone from the composted coffee grounds and spent brewer’s grains. These sugars are easily broken down by the microbes that exist in each bag of our compost and are given to the plant for Optimal Cannabis Carbohydrate Status for Photoperiod Transition. You can find the following ingredients in each batch, Composted coffee grounds, mushroom compost, cotton seed meal, cotton burr meal, poultry manure, spent brewer’s grain, wheat straw, gypsum, sphagnum peat moss, and sunflower hull ash.
Potassium Plant Reactions

The potassium in the Coffee-K is involved in many important biochemical reactions in cannabis plant production. Most of these functions are related to accelerated photosynthate production and improved photosynthesis.
Potassium is an essential plant nutrient and is required in large amounts for proper growth and reproduction of plants. Potassium is considered “mobile” in plants and can be utilized from old growth in plants to new growth. Potassium is considered second only to nitrogen, when it comes to nutrients needed by plants, and is commonly considered as the “quality nutrient.” Potassium is an essential plant nutrient and is required in large amounts for proper growth and reproduction of plants. Potassium is considered second only to nitrogen, when it comes to nutrients needed by plants, and is commonly considered as the “quality nutrient.”
Adenosine Triphosphate production is triggered by potassium to activate the biochemical enzymes that provide energy for chemical and physiological reactions in the plant.
K is also responsible for synthesis, movement, storage of starches, sugars, and fats in cannabis. It stimulates root growth, regulates plant stomata (opening and closing), transpiration and water use. These responsibilities maintain the internal pressure of the plant’s cells, ionic balance, and environmental resistance of diseases.
Without Potassium a plant cannot improve its carbohydrate status and thus lose out on the late-stage development that is required for larger yields during the flowering cycle of the plant. There is an old golf saying that fits well in this scenario, “Driving is for show. Putting is for dough.” Pretty much without the finish of a great flowering cycle and conversion of carbohydrates in your plants all of your grow was for show!
Roles of Potassium in Cannabis
Potassium or K+ in its ionic form, has many different roles in cannabis here is an overview:
-
- In Photosynthesis, potassium regulates the opening and closing of stomata, and therefore regulates CO2 uptake and transpiration.
-
- Potassium triggers activation of enzymes and is essential for production of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). ATP is an important energy source for many chemical processes taking place in plant issues.
-
- Potassium plays a major role in the regulation of water in plants (osmo-regulation). Both uptake of water through plant roots and its loss through the stomata are affected by potassium.
-
- Known to improve drought resistance.
-
- Protein and starch synthesis in plants require potassium as well. Potassium is essential at almost every step of the protein synthesis. In starch synthesis, the enzyme responsible for the process is activated by potassium.
-
- Activation of enzymes – potassium has an important role in the activation of many growth-related enzymes in plants.
Coffee Spelt With a K
What makes Coffee plus K unique is because of ability for the molecules to retain nutrients over extended periods of time compared to other synthetic fertilizers. Coffee-K not only has boosted potassium levels but trace amounts of nitrogen with a carbon to nitrogen ratio of about 20 to 1.
[iv] This slow-release potassium combined with cold brew coffee grounds is metabolized by the plant and microbes found in the soil to boost important functions within the plant during the flowering photoperiod. It provides a baseline for the chemical reactions that have to happen to form plant compounds, which include the following:
|
|
Potassium’s impact on the carbohydrate status of your cannabis plant can often go unnoticed.
Coffee-K in Your Cup
-
- Delivers an effective source of potassium with residual nutrients from the proprietary cold brew coffee compost.
-
- Creates photosynthetic integrity under stress conditions.
-
- Allows for an ideal baseline for all plant chemical reactions.
Thanks for reading and please visit our shop at http://www.comanchecompost.com to get started on your grow and stay social with us and reach out to our team if you have any questions about your soil and fertilizer needs.
Learn more about Comanche Compost Co. and stay up to date with other giveaways and cultivation pop up events around you!
Cannabis is literally found everywhere throughout the world but can only have great yields under certain conditions. You can grow outdoors, where you have the advantage of natural sunshine and atmospheric conditions or you can grow indoors, where it tends to be more reliable however, as you have a lot more control over that environment and increased capital costs. Whichever you choose, there are a number of principles to keep in mind for maximizing yields.
Before you plant anything make sure you know if you are cultivating an autoflowering or photoperiod strain. This is critical in planning your nutrient load and light loads for your plants to ensure that you have ideal conditions. Once you determine that you need to have reliable genetics from a reputable breeder. I would recommend Humboldt Seed Company due to their reliability, production, yield, and vigor. They tend to win at the Emerald Cup year after year and release outstanding genetics that focus on terpene and cannabinoid production. You can find their 2022 Emerald Cup Edition Seed by clicking on the image to the right or here. Once you order your seeds and prepare your set up you are ready to grow Good Medicine! Here are the 10 ways (in no order of importance) to improve the chances of your photoperiod dependent plant producing a great harvest!
[i] How is glucose made during photosynthesis used in plants? | AnswersDrive (worldseriesreports.com)
[ii] What is the glucose used for from photosynthesis? (treehozz.com)
[iii] Clearing up the Carb Controversy: Do Carbohydrate Supplements Really Produce Bigger Yields and Root Systems in Hydroponic Gardens. Julian Karadjov, PhD. November 10, 2011
[iv] Texas A&M study: Used coffee grounds can benefit turf – AgriLife Today (tamu.edu)



